Hernia
What is a Hernia
A hernia may occur whenever the muscles of the abdomen or your tummy develop a weak spot or a tear. Muscles normally hold the organs and surrounding tissues in place. An organ a such an intestine can push the abdominal lining through the weak spot and therefore form a balloon or a sac. Think of holding a balloon and squeezing it. It pops through your fingers.
The sac looks like a bulge under the skin when the patient is standing and can be the size of a marble. They can be made worse by a chronic
cough, heavy lifting or constipation. It causes pain and becomes worse over time.
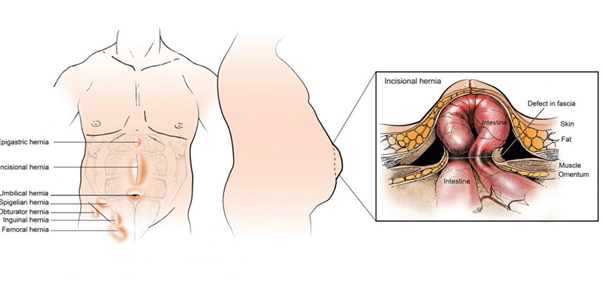
What Causes a Hernia
A hernia can be present at birth or it can develop over time due to strain and develop later in life.
Both Males and Females can develop a hernia. But are most common in men. 1 in 20men will develop a hernia at some point in their life. 9/10
hernias happen in the groin area and are called inguinal or femoral hernias. Incisional hernias are from a
previous operation site, umbilical is near the belly button and epigastric hernias are midline below the breast bone.
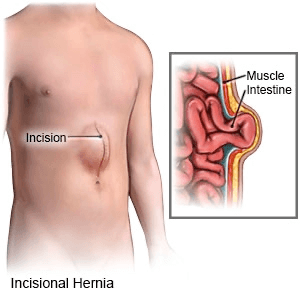
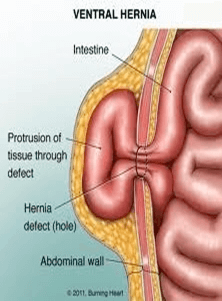
Repair
Hernia repair is a very common operation. Special belts can be used to support the hernia but surgery is the best option. If neglected a hernia will usually get worse and increase in size. Occasionally it can lead to complications, strangulation of the intestine. Emergency treatment is then required.
Laparoscopic or Open hernia repair are the two different methods of repairing hernias, the use of a thin soft mesh can make the hernia repair stronger and last longer, tissue grows over the mesh as the area heals and the mesh becomes part of the body giving support and strength to the abdominal muscles.
Hernia Repair Risks
All surgical procedures have risks and complications, despite the highest standards of surgical practice, these can have permanent effects. It is not usual for a surgeon to outline every possible risk and or rare complication of an operation but you should have enough information to form your own opinion and judgment. Weigh up the benefits risks and limitations of surgery. Please discuss these with your surgeon. Patients with conditions such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, asthma amongst other conditions can hinder surgery and make you more susceptible to complications.
General risks include; hernia re occurrence, thrombosis, Stroke, Blood clots. These are all very serious and require immediate attention. Infection can occur and mostly in diabetic patients or those on Prednisone or Prednisolone. A keloid can form (raised skin or scar) these can be irregular in shape and can become itchy and inflamed. Most people are not predisposed to keloids, some people are and they can be annoying but of no threat to your health. Chronic nerve pain can occur due to the involvement of a nerve in the repair. Rarely blood supply to the testicle can be affected after a groin hernia repair.
Post Surgery Alerts
You must take it easy for 2-4-6 weeks post Hernia Repair Surgery. You will have a review appointment with Dr van Schoor 2-4-6 weeks depending on your surgery. Inform New England Surgical, Dr van Schoor or your GP immediately if you suffer from the following side effects; fever or chills temp higher that 38) an incision that drains for more than one day, increasing pain or redness around the incision site. Feel dizzy, faint or short of breath. Any concerns that you have regarding your surgery. If you cannot contact us go to your family doctor or present to emergency department at the nearest hospital.
